a reference guide to surviving nature outdoor preparation and remedies
Category : Guide
Essential Outdoor Survival Skills
Navigating with a compass and map is crucial․ Starting a fire safely and efficiently is vital․ Building a sturdy shelter protects from harsh weather․ Finding and purifying water sources ensures hydration․ These skills are fundamental for outdoor survival․
1․1 Navigation and Orienteering
Navigating and orienteering are critical skills for outdoor survival․ mastered with map and compass․ Use a compass to determine direction and identify landmarks for guidance․ Maps provide details on terrain, trails, and water sources, helping you stay on course․ Practice using natural signs, like the North Star, to navigate without tools․ Always double-check your bearings and adjust for magnetic declination․ If lost, stay put and use smoked signals or bright objects to attract help․ Mastering these techniques ensures safety and confidence in the wild․
Using the sun’s position can help determine direction when no tools are available․ Marking landmarks and pacing regularly can prevent disorientation․ In challenging environments, stay calm and instincts to find your way․ Practice these skills before venturing out
1․2 Starting and Maintaining a Fire
Starting and maintaining a fire is a critical skill for outdoor survival․ Always carry fire-starting tools like lighters, matches, or fire steel in your survival kit․ Choose a safe location, clear of debris, and protect it from wind․ Gather tinder, kindling, and fuel wood to build a reliable fire․ Maintain the fire by carefully adding kindling and larger combustibles as needed․
A fire serves multiple purposes: providing warmth, cooking food, purifying water, and signaling for help․ Learn to start fires in various conditions, such as wet environments or windy situations․ Always prioritize fire safety and avoid overloading the fire with too much fuel, as this can cause it to burn out quickly․ Practice these techniques regularly to ensure readiness in emergency situations․
1․3 Building a Shelter
Building a shelter is essential for survival in the wild․ Choose a safe location, away from hazards like falling debris or flood-prone areas․ Use natural materials such as branches, leaves, and vines to construct a sturdy shelter․ Build a framework to support the roof and walls, ensuring stability and protection from the elements․
Line the floor with insulating materials like pine needles or grass to stay dry․ Create an entrance that can be closed to trap warmth․ Practice constructing shelters in different terrains to adapt to various conditions․ Remember to secure your shelter against strong winds or heavy rain, and maintain it regularly to prevent collapse or damage․
1․4 Finding and Purifying Water
Finding and purifying water is a critical outdoor survival skill․ Start by locating natural water sources like streams, rivers, or lakes․ Use a clean container to collect water, ensuring it is free from visible debris․ If no running water is available, gather rainwater or look for water in natural depressions or wetlands․ Always prioritize finding a clean source to minimize contamination risks․
To purify water, boil it for at least 1 minute to kill harmful pathogens․ If boiling is not possible, use a portable water filter or add purification tablets․ Avoid drinking untreated water, as it may containborne illnesses․ Carry a water filtration system in your survival kit for on-the-go purification․ Remember, staying hydrated is essential for survival, so locate and purify water consistently while in the wild․
Outdoor Survival Preparation
Packing a survival kit with essentials ensures readiness for unexpected situations․ Select gear suited to your environment and activity․ Prepare for weather extremes by including layers, rain gear, and insulation․ Carry emergency tools like a multi-tool, flashlight, and solar charger for communication and navigation․
2․1 Packing a Survival Kit
Packing a survival kit is crucial for outdoor adventures․ Include essentials like a multitool, first-aid kit, fire starter, and emergency blanket․ Add a solar charger to power devices like phones for communication․ Choose gear suited to your environment, such as hand warmers for cold climates or mosquito repellent for jungle settings․ Always test your preparedness in realistic scenarios to ensure you know how to use your kit effectively․

2․2 Selecting the Right Gear
Selecting the right outdoor gear ensures safety and comfort in various conditions․ Choose a reliable tent or tarp for shelter, along with durable clothing suited to the climate․ Opt for high-quality navigation tools, such as a compass and map, to avoid getting lost․ Include a headlamp or flashlight with extra batteries for visibility․ Prioritize gear that fits your specific environment, such as insulated clothing for cold climates or lightweight options for warmer regions․ Always carry a first-aid kit and essential tools like a multi-tool or knife․ Test your equipment beforehand to ensure it functions properly, reducing the risk of malfunctions in critical situations․
2․3 Weather Preparedness
Weather Preparedness
Staying informed about the weather is crucial for outdoor safety․ Always check forecasts before heading out and prepare for sudden changes․ Dress in layers to adapt to varying temperatures and protect against wind, rain, or snow․ Carry a lightweight compass and map to navigate in low visibility․ Waterproof your gear and pack an emergency shelter like a space blanket or bivy sack․ Stay dry by avoiding prolonged exposure to wet conditions and use a tarp or rainfly to stay protected․ Monitor humidity and temperature to prevent dehydration or heat-related issues․ By anticipating weather challenges, you enhance your ability to stay safe and comfortable in any environment․
2․4 Emergency Communication Tools
Incorporating reliable emergency communication tools into your outdoor preparation is essential․ Include a charged cell phone, equipped with a solar charger, to maintain connectivity during prolonged trips․ Carry a compact, water-resistant flashlight with extra batteries for visibility and signaling․ A whistle is a simple yet effective tool for attracting attention․ Additionally, pack a personal locator beacon or GPS-enabled device for emergencies in remote areas․ Prioritize testing these tools before your expedition and ensure they are easily accessible in your survival kit․ By integrating these communication tools into your preparation, you enhance your ability to stay connected and secure assistance when needed․
First Aid and Natural Remedies
Mastering first aid and natural remedies is crucial in outdoor survival․ Learn to treat wounds, recognize poisonous plants, and create healing poultices from available resources․ Knowing how to identify edible plants and use them for sustenance is also vital․ These skills ensure safety and well-being when help may be hours or days away․

3․1 Basic First Aid Techniques
Mastery of basic first aid is essential for outdoor survival․ Key techniques include cleaning and bandaging wounds to prevent infection, stopping bleeding by applying direct pressure, and immobilizing injured limbs to prevent further damage․ Learn to recognize signs of shock and how to keep a victim calm and comfortable․ Knowing how to treat burns, sprains, and minor injuries can mean the difference between life and death in remote environments․ Always carry a first aid kit with essential supplies and practice these skills regularly to ensure readiness in emergencies․

3․2 Identifying and Using Edible Plants
Identifying edible plants in the wild is a critical skill for survival․ Begin by learning to distinguish between safe and poisonous varieties through careful observation of plant features like leaves, stems, and flowers․ Start by testing a small portion of the plant to check for adverse reactions before consuming larger quantities․ Common edible plants include wild berries, dandelions, and cattails, which can provide essential nutrients and energy․ Always prioritize plants that you can confidently identify to avoid accidental poisoning․ When foraging, focus on areas with clean soil and away from toxic environments․ Using edible plants can supplement your food supply and help you sustain yourself in the wilderness․
3․3 Making Natural Painkillers and Healing Poultices
Natural painkillers and healing poultices can be created using plants found in the wild․ Willow bark tea, for example, contains salicin, a natural aspirin-like compound that reduces pain and inflammation․
For poultices, bruised plantain leaves or crushed mullein can be applied to wounds to soothe irritation and promote healing․
Additionally, mixing clay with warm water forms a cooling poultice that can ease swelling and discomfort․
When preparing these remedies, always ensure the plants are correctly identified and free from contaminants․
These natural solutions can provide temporary relief in the absence of modern medications, but seek professional medical help when possible․
3․4 Treating Common Outdoor Injuries
When injuries occur outdoors, prompt and proper treatment is essential․ Cuts and scrapes should be cleaned with water and dressed with clean cloth or bandages to prevent infection․
For sprains, elevate the injured area and immobilize it using a splint or makeshift support․
Burns can be cooled with water, and aloe vera or sterile ointment can soothe the affected skin․
Bleeding can be controlled using direct pressure while elevating the wound above heart level․
Snakebites require immobilization of the limb and avoiding unnecessary movement to slow venom spread․
Always carry a first aid kit and know how to use its contents effectively․
Natural remedies like yarrow for clotting or plantain for inflammation can complement basic first aid․
Stay calm, assess the situation, and prioritize safe evacuation to professional medical care when possible․
Psychological and Mental Preparation
Mentally prepare for survival by managing fear and anxiety․ Build resilience through adaptability and a positive mindset․ Stay calm under pressure by focusing on task prioritization․ Use natural remedies, like aromatic plants, to reduce stress․ Develop coping strategies to maintain mental stability in challenging situations․

4․1 Managing Fear and Anxiety in Survival Situations
Managing Fear and Anxiety in Survival Situations
In survival scenarios, fear and anxiety can impair judgment and hinder decision-making․ Managing these feelings is critical for maintaining focus and effectively addressing challenges․ Practice controlled breathing exercises to calm your mind and reduce panic․ Focus on the present moment, breaking tasks into manageable steps․ Avoid overthinking the situation or worst-case scenarios․ Develop a mental checklist to prioritize needs, ensuring clarity of thought․ Understanding your emotional responses and acknowledging your fears can help you regain control․ Trust in your preparedness and training to build confidence under pressure․ By mastering emotional resilience, you can navigate even the most daunting outdoor survival situations with composure․ Ultimately, fear is a natural response; your ability to manage it determines your success․ Prepare mentally by rehearsing scenarios, visualizing outcomes, and reinforcing a positive mindset․ Embrace the situation as an opportunity to strengthen your emotional fortitude and adaptability․ Remember, survival is as much about mindset as it is about skills․ Train your brain to stay calm, think clearly, and act decisively․
4․2 Developing a Positive Mental Attitude
A positive mental attitude is vital for surviving challenging outdoor situations․ cultivate optimism by focusing on solutions rather than obstacles․ Train yourself to reframe negative thoughts into proactive ones․ Practice visualization techniques to mentally prepare for potential scenarios․ Embrace challenges as opportunities to grow and thrive․ Surround yourself with uplifting stories of others’ survival successes․ Develop a mindset that seeks to problem-solve creatively․ Even in dire circumstances, maintain hope and believe in your ability to overcome․ Stay calm, remain positive, and view every obstacle as a step toward resilience․ Your mental state can determine your ability to endure and emerge stronger from any situation․
4․3 Staying Calm Under Pressure
Remaining calm is critical when faced with high-pressure survival situations․ Take slow, deep breaths to manage your stress response․ Focus on one task at a time, breaking problems into smaller, manageable steps․ Avoid panicking by staying present and assessing the situation objectively․ A clear mind allows you to make logical decisions and adapt to challenges effectively․ Practice mindfulness and visualization techniques to build emotional resilience․ Remember, staying calm prevents errors and ensures you can think clearly under duress․ This mental fortitude is essential for overcoming obstacles and ensuring your survival in difficult outdoor conditions․

4․4 Building Resilience and Adaptability
Resilience and adaptability are vital for surviving outdoor adventures․ Practice facing challenges with a growth mindset, turning obstacles into opportunities to learn and improve․ Develop problem-solving skills to address unexpected situations calmly and efficiently․ Prepare for the unknown by simulating realistic scenarios and testing your skills in diverse environments․ Embrace change and remain open to new strategies for overcoming difficulties․ Resilience fosters the ability to recover from setbacks and adapt to ever-changing conditions, ensuring your survival and success in the wild․ With practice, you can cultivate mental toughness and become a more capable and resourceful survivor․

Advanced Survival Techniques
Bushcraft skills emphasize self-reliance in the wild, including making tools and natural remedies․ Trapping and foraging for food require knowledge of local ecosystems and sustainable practices․ Signaling for help involves creative use of resources and maximizing visibility․ Mastering these techniques ensures you can adapt to extreme environments and survive longer-term challenges in the wilderness․
5․1 Bushcraft Skills
Bushcraft skills are essential for thriving in wilderness environments․ Mastering knife-making from natural materials allows you to craft tools for cutting, carving, and building․ Constructing shelter from branches and leaves ensures protection from the elements․ Learning to create cordage from plant fibers enables you to tie secure knots and build structures․ Bushcraft also involves identifying edible plants and crafting natural remedies․ Knowing how to purify water using filtration or heat ensures a safe supply․ These techniques allow you to adapt to diverse ecosystems and work with available resources․ Practicing bushcraft builds resilience and self-reliance in remote, challenging settings․

5․2 Trapping and Foraging
Trapping and foraging are vital skills for outdoor survival․ Constructing simple yet effective traps from natural materials allows you to catch small game or fish, ensuring a sustainable food supply․ Learning to identify edible plants and mushrooms is essential for foraging safely, as many wild species can be poisonous․ Never forage without proper knowledge or local guides․ Foraging for wild berries, nuts, and herbs provides natural remedies and nutrients․ Always respect local wildlife regulations to avoid harm to ecosystems or legal consequences․ Improvising tools from the environment enables successful trapping and foraging in remote areas, while preparing gathered food ensures safety and sustenance․ These skills promote resilience and self-reliance in the wilderness, making them a cornerstone of advanced survival techniques․
5․3 Signaling for Help
Signaling for help is a critical skill when stranded in the wilderness․ Use a mirror or reflective object to flash light toward rescue planes or helicopters․ Create large, visible ground signals using rocks, logs, or branches_spell out your message or distress signals like SOS․ Build smoky fires during the day or add green vegetation to create thick, visible smoke․ At night, use a flashlight or flare to send distress signals․ Stay elevated in open areas to increase visibility․ Utilize noise-making devices like whistles or banging objects to attract attention․ Always prioritize safe and sustainable signaling methods to conserve resources and avoid unintended risks․ These techniques enhance your chances of being located and rescued efficiently․
5․4 Surviving in Extreme Environments
Surviving in extreme environments requires adaptability and preparedness․ Packing a survival kit tailored to harsh conditions is essential․ In extreme cold, layer clothing, use hand warmers, and build insulated shelters․ In arid deserts, conserve water, avoid daytime heat, and navigate using natural landmarks․ At high altitudes, acclimate slowly, stay hydrated, and avoid overexertion to prevent altitude sickness․ Always prioritize shelter construction to protect from elements like wind or snow․ Use signaling tools to enhance visibility for rescue․ Test your bushcraft skills in realistic scenarios to ensure readiness․ Staying calm and resourceful in extreme conditions increases your chances of survival․ These techniques help you navigate and endure even the most challenging environments effectively․

Outdoor Safety and Risk Management
Avoiding hazards like unstable terrain and wildlife is crucial․ Preventing hypothermia by layering clothes and staying dry is essential․ Navigating dangerous areas with caution protects against accidents․ Staying calm and prepared helps manage risks and ensures safety in the outdoors․
6․1 Avoiding Common Outdoor Dangers
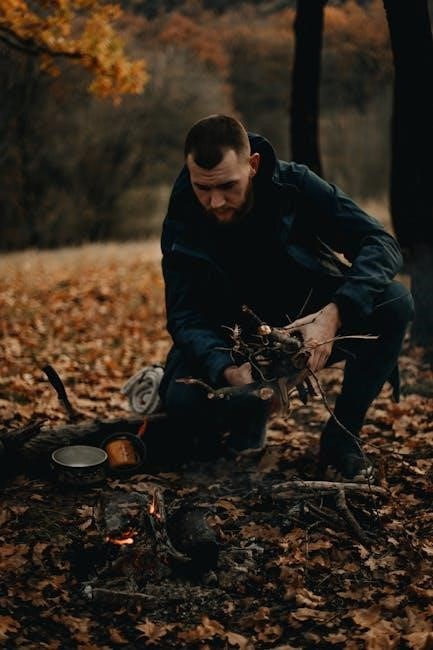

Avoiding common outdoor dangers begins with recognizing potential hazards like poisonous plants, venomous animals, and unstable terrain․ Stay alert to your surroundings and avoid risky paths or areas with visible dangers․ Keep a safe distance from wildlife to prevent unexpected encounters․ Always check for signs of hazards, such as sharp rocks, steep drops, or areas prone to landslides․ Pro tip: Carry a map and compass or GPS device to navigate safely․ Pay attention to weather changes, as sudden storms or temperature shifts can create unexpected risks․ Pack essential safety gear, including a headlamp, sturdy footwear, and a first-aid kit, to stay prepared․ By being cautious and avoiding complacency, you can minimize risks and ensure a safer outdoor experience․
6․2 Preventing and Treating Hypothermia
Hypothermia occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce it, often due to cold, wet conditions․ Prevent it by dressing in layers, using moisture-wicking fabrics, and staying dry․ Avoid overexertion that leads to sweating․ On preventing hypothermia, always carry emergency gear like hand warmers and space blankets․ If signs of hypothermia appear, such as uncontrollable shivering or confusion, act immediately; Move the person to shelter, remove wet clothing, and provide warm drinks or food․ Use a heat source or body-to-body contact to slowly rewarm the person․ Avoid placing them in hot water or exposing them to extreme temperatures, which can shock the system․ Featured tip: Always pack an emergency blanket and high-energy snacks to stay warm and fueled in cold environments․
6․3 Surviving Animal Encounters
Encounters with wildlife can be dangerous, but proper preparation and awareness can reduce risks․ Avoid attracting animals by securing food and avoiding strong odors․ Stay calm and do not run if approached; maintain a respectful distance․ Face the animal and back away slowly․ Carry deterrent tools, such as bear spray or a walking stick, and make noise to alert animals to your presence․ Avoid sudden movements that may trigger a defensive response․ If attacked, fight back using rocks, sticks, or anything at hand․ Consider the environment and barriers that can provide protection․ Featured tip: Research local wildlife and their behaviors to prepare for potential encounters․ Always prioritize safety and avoid confrontations․
6․4 Navigating Dangerous Terrain
Navigating dangerous terrain requires careful preparation and awareness of potential hazards․ Before heading out, research the route and identify challenges like steep slopes, loose rocks, or unstable ground․ Wear sturdy, supportive footwear and pack reflective gear for visibility․ Use a map and compass or GPS to stay on course and avoid getting lost․ If crossing rivers, test the water’s depth and current; never wade into areas where the water is too deep or fast-moving․ Stay alert for signs of natural hazards, such as landslide zones or collapsing cliffs․ Avoid hiking at night in unfamiliar terrain to reduce the risk of accidents․ Always notify someone of your plans and carry a first-aid kit․ Featured tip: Practice balance and stability techniques to prevent falls on uneven ground․ Navigating dangerous terrain demands focus, caution, and respect for nature’s power․